Kubernetes API
The Kubernetes API stands at the heart of a Kubernetes cluster, serving as the critical pathway for all forms of communication, both from users and within the cluster's components. This guide breaks down the essential aspects of how the Kubernetes API operates, ensuring secure and controlled interactions with the cluster.
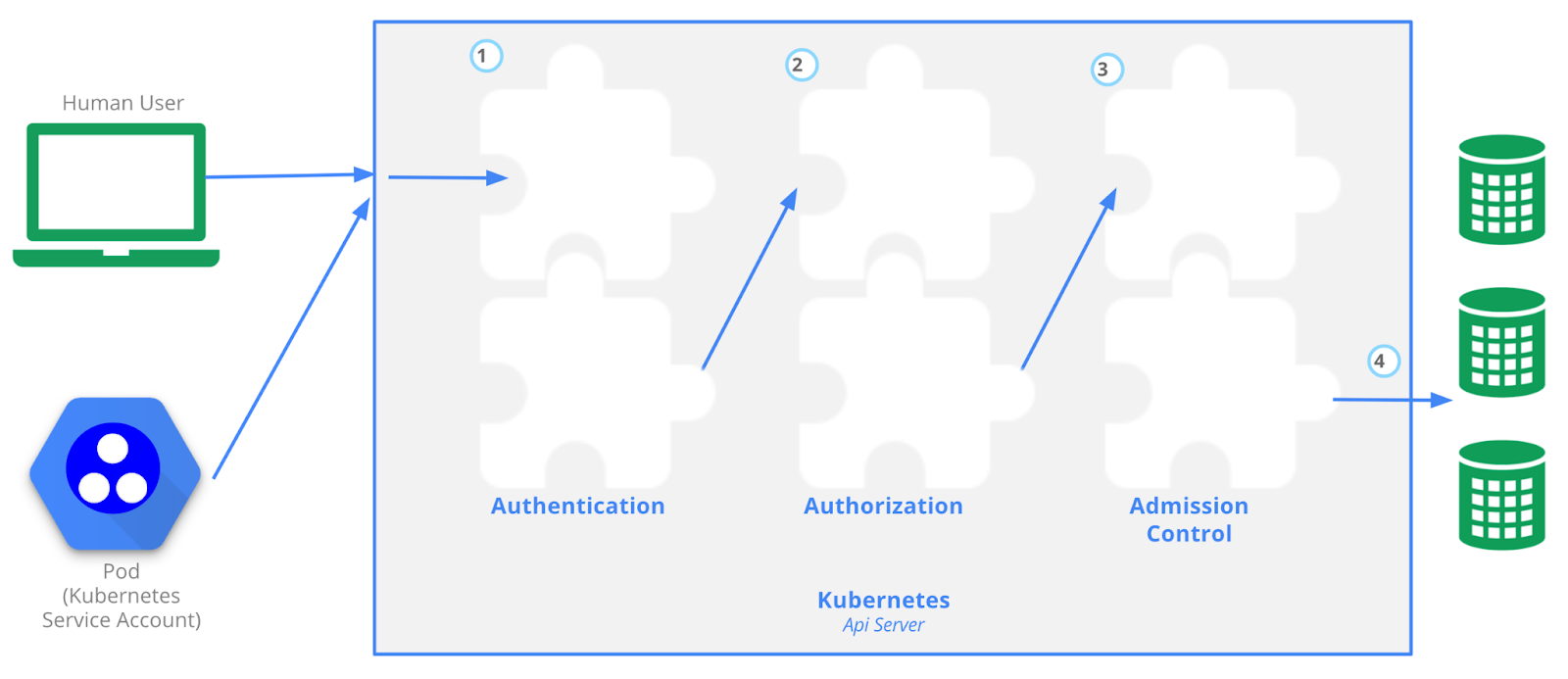
Key Stages of Interaction with the Kubernetes API:
1. Authentication:
What It Is: The first step in interacting with the Kubernetes API requires proving who you are.
How It's Done: This can be through digital certificates (X.509) or external identity systems. While Kubernetes itself doesn't manage user identities directly, it allows technical users (like services and applications) to authenticate via Service Accounts.
2. Authorization:
What It Is: Once authenticated, the system then determines what actions you're allowed to perform.
How It Works: Kubernetes employs Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to define permissions for different roles within the cluster, ensuring users and services have access only to what they need.
3. Admission Control:
What It Is: The final gatekeeper before a request is executed. This step allows for further validation or modification of the request.
Use Cases: For instance, admission controllers can prevent the use of unauthorized container images. External tools, like Open Policy Agent, can be integrated to manage these policies more flexibly.
The API Itself:
Nature of the API: The Kubernetes API is RESTful, meaning it follows the REST (Representational State Transfer) standards and principles, facilitating easy and standardized interaction over HTTPS.
Functionality: Through this API, users and services can perform a wide range of actions, such as creating, modifying, deleting, or fetching resources within the Kubernetes environment.
Understanding these elements of the Kubernetes API is crucial for anyone looking to interact with a Kubernetes cluster effectively. Whether you’re deploying new applications, managing cluster resources, or setting up security protocols, the API serves as your main interface with the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Last updated