Fundamentals
Cloud native architecture is a modern approach to software design that prioritizes cost efficiency, reliability, and quick market delivery. It encompasses a blend of cultural norms, technology choices, and architectural designs.
The term "cloud native" varies in definition, focusing either on technology or culture. According to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation, cloud native technologies allow for the creation and operation of scalable applications across diverse environments like public, private, or hybrid clouds. Key elements include containers, service meshes, microservices, immutable infrastructure, and declarative APIs. These elements support systems that are loosely connected, easy to manage, resilient, and observable. They also enable frequent, impactful, and predictable updates with minimal effort.
Contrastingly, traditional applications, often called legacy applications, usually adopt a monolithic design. In this design, all functionalities are encapsulated in a single, self-contained unit. For example, an E-Commerce platform would have everything from the user interface to order processing in one codebase and binary file. While simple in development and deployment, this model struggles with complexity management, rapid changes, scalability, and collaborative development.
Cloud native architecture addresses these challenges by decomposing applications into smaller, more manageable pieces, known as microservices. Each microservice is independent and performs a specific function. For instance, an E-Commerce site could have separate microservices for user interface, checkout, etc. This architecture allows for distributed ownership and scalability. Teams can independently manage different application functions, and services under high demand, like shopping carts and checkout systems, can be scaled as needed.
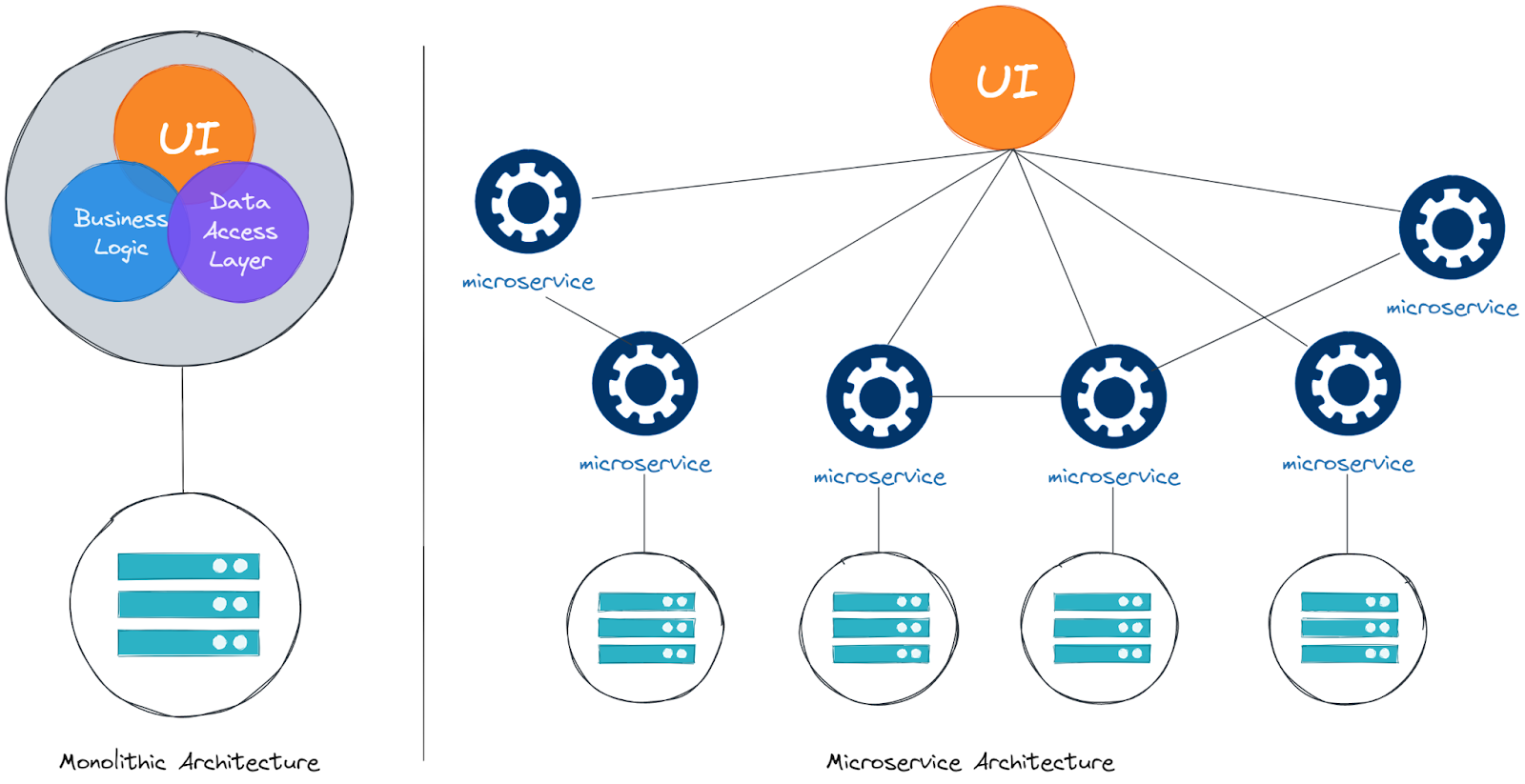
While cloud native architecture offers significant benefits, it also introduces complexity and demands specific requirements for effective integration.
Last updated