Autoscaling
Autoscaling is a key concept in cloud computing where resources automatically adjust to the current demand. This dynamic scaling can be based on various metrics, such as CPU and memory usage, or even time-based or business-specific metrics.
Types of Scaling
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling involves adding more computing resources, like instances of an application process, virtual machines, or even physical hardware like server racks. It's akin to asking friends to help carry a heavy object – distributing the load among more people.
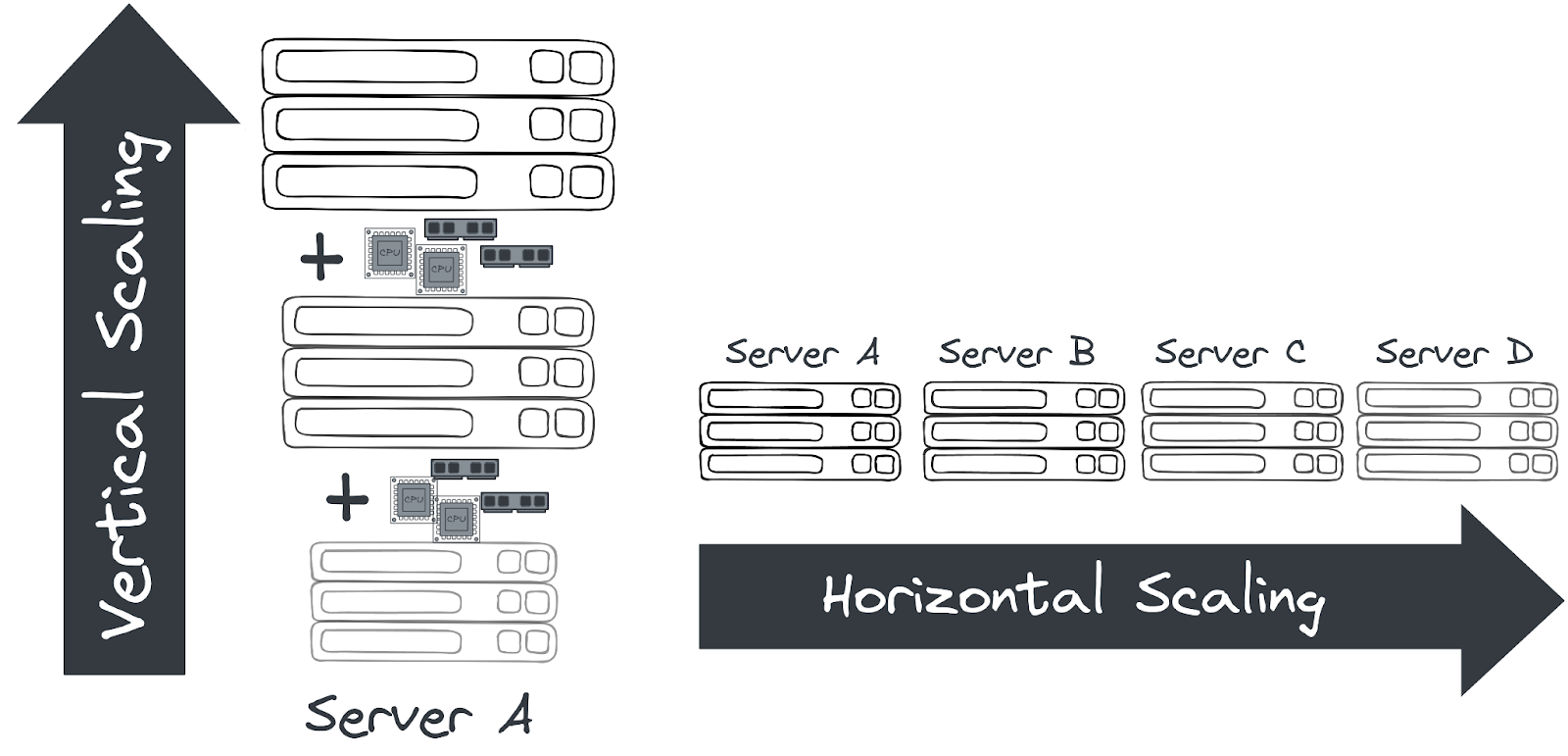
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, on the other hand, means enhancing the capacity of existing hardware. It's like building muscle to lift heavier objects alone, but there's a limit to how much strength (or hardware capacity) one can develop.
Implementing Autoscaling
To set up autoscaling, you need to define minimum and maximum limits for resources (like VMs or containers) and choose a metric that triggers scaling. Fine-tuning these settings usually involves extensive load testing to understand how the application behaves under different conditions.
Advantages in Cloud Environments
Cloud-based autoscaling is particularly effective due to on-demand, usage-based pricing models. It allows for rapid provisioning of a large number of resources or even scaling down to zero when they're temporarily unnecessary.
Broad Applicability
While initial scaling efforts might not be automated, the capacity to scale is crucial for increasing the availability and resilience of services, even in more traditional setups. This flexibility is a significant advantage of cloud-native environments.
Last updated